Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are a set of numerical values that describe the unique quantum state of an electron in an atom. The four quantum numbers include the principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), magnetic quantum number (ml), and spin quantum number (ms). Each of these numbers provides specific information about the electron's energy level, shape, orientation, and spin.
Recommended video:
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level or shell of an electron in an atom. It can take positive integer values (n = 1, 2, 3, ...), with higher values corresponding to electrons that are further from the nucleus and have higher energy. The value of n determines the size and energy of the orbital.
Recommended video:
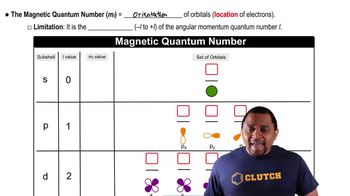
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l) and Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
The azimuthal quantum number (l) defines the shape of the orbital and can take integer values from 0 to (n-1). Each value of l corresponds to a specific type of orbital (s, p, d, f). The magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of the orbital in space and can take values from -l to +l, including zero. Together, l and ml help to specify the spatial distribution of electrons within an atom.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance