Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Equations
Chemical equations represent the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. They must be balanced to obey the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Each element's number of atoms must be the same on both sides of the equation, ensuring that the total mass remains constant.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations
Formation Reactions
A formation reaction is a specific type of chemical reaction where a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. For example, when writing the formation reaction for uranium hexafluoride, one must consider the elemental forms of uranium and fluorine at standard conditions, which are solid uranium and gaseous fluorine, respectively.
Recommended video:
Uranium Hexafluoride (UF6)
Uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is a compound used in the uranium enrichment process. It consists of one uranium atom bonded to six fluorine atoms. Understanding its formation requires knowledge of the oxidation states of uranium and the properties of fluorine, as well as the conditions under which UF6 is stable, particularly its solid state at room temperature.
Recommended video:
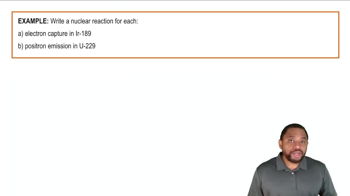
Electron Capture & Positron Emission Reaction Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance