For each of the following, (i) give the systematic name of the compound and specify the oxidation state of the transition metal, (ii) draw a crystal field energy-level diagram and assign the d electrons to orbitals, (iii) indicate whether the complex is high-spin or low-spin (for d4 - d7 complexes), and (iv) specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(a) (NH4)[Cr(H2O)6](SO4)2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Coordination Compounds
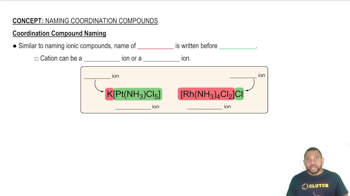
Crystal Field Theory

Spin States and Unpaired Electrons

In octahedral complexes, the choice between high-spin and low-spin electron configurations arises only for d4 - d7 complexes. Explain.
For each of the following, (i) give the systematic name of the compound and specify the oxidation state of the transition metal, (ii) draw a crystal field energy-level diagram and assign the d electrons to orbitals, (iii) indicate whether the complex is high-spin or low-spin (for d4 - d7 complexes), and (iv) specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(c) [Ni(NH3)4(H2O)2](NO3)2
For each of the following, (i) give the systematic name of the compound and specify the oxidation state of the transition metal, (ii) draw a crystal field energy-level diagram and assign the d electrons to orbitals, (iii) indicate whether the complex is high-spin or low-spin (for d4 - d7 complexes), and (iv) specify the number of unpaired electrons. (d) K4[Os(CN)6]
For each of the following, (i) give the systematic name of the compound and specify the oxidation state of the transition metal, (ii) draw a crystal field energy-level diagram and assign the d electrons to orbitals, (iii) indicate whether the complex is high-spin or low-spin (for d4 - d7 complexes), and (iv) specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(e) [Pt(NH3)4](ClO4)2
