Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
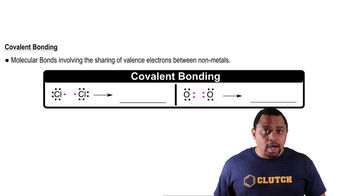
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, typically between nonmetals. This type of bonding allows atoms to achieve a full outer shell of electrons, leading to greater stability. Compounds with covalent bonds often have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds and can exist as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature.
Recommended video:
Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of charged ions that attract each other. In contrast, covalent compounds involve the sharing of electrons. Understanding the difference between these types of bonding is crucial for predicting the properties and behaviors of various compounds, including their solubility and conductivity.
Recommended video:
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a bond. In general, nonmetals have higher electronegativities than metals, which influences whether a bond will be ionic or covalent. When two atoms with similar electronegativities bond, they are more likely to form covalent bonds, while a significant difference typically leads to ionic bonding.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance