Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Radioactive Decay
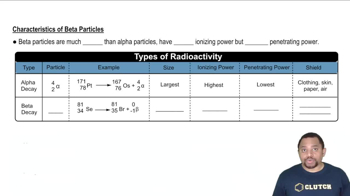
Radioactive decay is a process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This can occur in various forms, including alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay, each resulting in the transformation of the original nucleus into a different element or isotope. Understanding the type of decay is crucial for predicting the particles produced.
Recommended video:
Rate of Radioactive Decay
Alpha Particles
Alpha particles are a type of radiation consisting of two protons and two neutrons, essentially a helium nucleus. They are emitted during alpha decay, a common form of radioactive decay for heavy elements. The emission of alpha particles decreases the atomic number of the original element by two, resulting in a new element.
Recommended video:
Characteristics of Alpha Particles
Beta Particles
Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted during beta decay. In beta minus decay, a neutron is transformed into a proton, emitting an electron and an antineutrino, while in beta plus decay, a proton is converted into a neutron, emitting a positron and a neutrino. This process changes the atomic number of the element, leading to the formation of a different element.
Recommended video:
Characteristics of Beta Particles
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance