Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nuclear Decay Processes
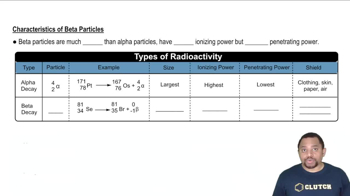
Nuclear decay processes refer to the mechanisms by which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy and particles to achieve stability. The primary types include alpha (α) decay, where an alpha particle is emitted; beta (β) decay, which involves the emission of beta particles (electrons or positrons); and electron capture, where an electron is absorbed by the nucleus, converting a proton into a neutron.
Recommended video:
Balanced Nuclear Equations
A balanced nuclear equation represents the transformation of one element into another during a nuclear reaction, ensuring that the total number of protons and neutrons is conserved. This involves adjusting the atomic numbers and mass numbers of the reactants and products to reflect the particles emitted or absorbed during the decay process.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations
Alpha and Beta Particles
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons, making them relatively heavy and positively charged, while beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted during beta decay. Understanding the nature of these particles is crucial for writing accurate nuclear equations, as they determine the changes in atomic and mass numbers during the decay processes.
Recommended video:
Characteristics of Beta Particles
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance