Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. In an electrolytic cell, an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, causing the decomposition of the compound into its constituent ions. This process occurs at inert electrodes, which do not participate in the reaction but facilitate the transfer of electrons.
Recommended video:
Ionic Compounds in Aqueous Solution
When ionic compounds like KCl are dissolved in water, they dissociate into their respective ions (K⁺ and Cl⁻). In electrolysis, these ions migrate towards the electrodes: cations move towards the cathode (negative electrode) and anions towards the anode (positive electrode). The behavior of these ions during electrolysis is crucial for predicting the products formed.
Recommended video:
Types of Aqueous Solutions
Electrode Reactions
At the electrodes during electrolysis, specific reactions occur based on the ions present and their standard electrode potentials. At the cathode, reduction occurs, typically involving the gain of electrons by cations, while at the anode, oxidation occurs, often involving the loss of electrons by anions. The products formed depend on the nature of the ions and the conditions of the electrolysis.
Recommended video:
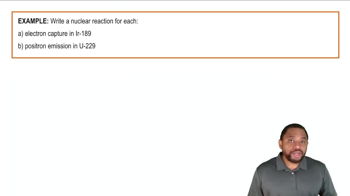
Electron Capture & Positron Emission Reaction Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance