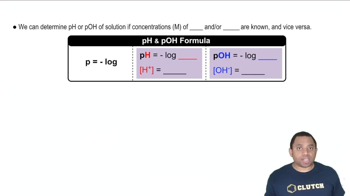
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Solutions
A buffer solution is a system that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The ability of a buffer to maintain pH is crucial in many chemical and biological processes.
Recommended video:
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a buffer solution to the concentration of its acid and conjugate base. It is expressed as pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]), where pKa is the acid dissociation constant. This equation helps determine the appropriate ratio of acid to base needed to achieve a desired pH.
Recommended video:
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pKa and pH Relationship
The pKa value of an acid indicates the strength of the acid; lower pKa values correspond to stronger acids. For a buffer to effectively maintain a specific pH, the pKa of the weak acid should be close to the desired pH. In this case, a buffer with a pKa around 7.00 is ideal for achieving a pH of 7.00.
Recommended video: