Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Reaction Order
The reaction order is a key concept in chemical kinetics that indicates the relationship between the concentration of reactants and the rate of the reaction. It is determined experimentally and can be zero, first, second, or higher order, depending on how the rate changes with varying concentrations. For the given reaction, understanding the order helps in formulating the rate law, which is essential for calculating the rate constant.
Recommended video:
Rate Law
The rate law expresses the rate of a chemical reaction as a function of the concentration of its reactants, each raised to a power corresponding to its order in the reaction. For the decomposition of AB2, the rate law can be written as rate = k[AB2]^n, where k is the rate constant and n is the reaction order. Determining the rate law is crucial for finding the rate constant through experimental data.
Recommended video:
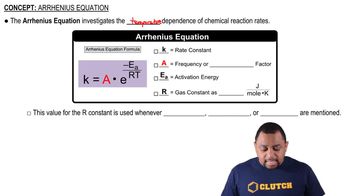
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant (k) of a reaction to the temperature (T) and activation energy (Ea) of the reaction. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where A is the pre-exponential factor, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation is vital for determining the rate constant at different temperatures and understanding how temperature influences reaction rates.
Recommended video: