Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Activation Energy
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to transform into products. Even if two reactions have the same activation energy, other factors can influence their rates, such as the frequency of collisions and the orientation of reactants during those collisions.
Recommended video:
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a reaction refers to how quickly reactants are converted into products. It is influenced by several factors, including concentration, temperature, and the presence of catalysts. In this case, even with the same activation energy, differences in the rate can arise from variations in these factors, particularly the frequency of effective collisions between reactant molecules.
Recommended video:
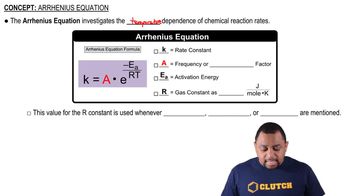
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation describes the relationship between the rate constant of a reaction and temperature, incorporating activation energy. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. The pre-exponential factor can vary significantly between reactions, leading to differences in rates even when activation energies are identical.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance