Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Parts Per Million (ppm)
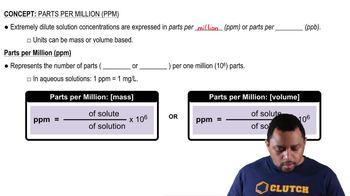
Parts per million (ppm) is a unit of measurement that expresses the concentration of a substance in a solution. It indicates how many parts of a solute are present in one million parts of the solution. For example, a concentration of 1.5 ppm means there are 1.5 grams of solute in one million grams of solution, which is crucial for calculating the required mass of sodium fluoride in this context.
Recommended video:
Molar Mass and Stoichiometry
Understanding molar mass is essential for converting between grams and moles of a substance. Sodium fluoride (NaF) has a molar mass of approximately 42 g/mol. Stoichiometry allows us to relate the mass of NaF needed to achieve the desired fluoride ion concentration in the water, enabling accurate calculations based on the ppm value.
Recommended video:
Dilution and Solution Preparation
Dilution is the process of reducing the concentration of a solute in a solution, typically by adding more solvent. In this case, knowing the volume of water (750 L) and the desired concentration (1.5 ppm) allows us to calculate the total mass of fluoride needed and subsequently determine how much sodium fluoride must be added to achieve that concentration in the water.
Recommended video:
Solution Dilution Process
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance