Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
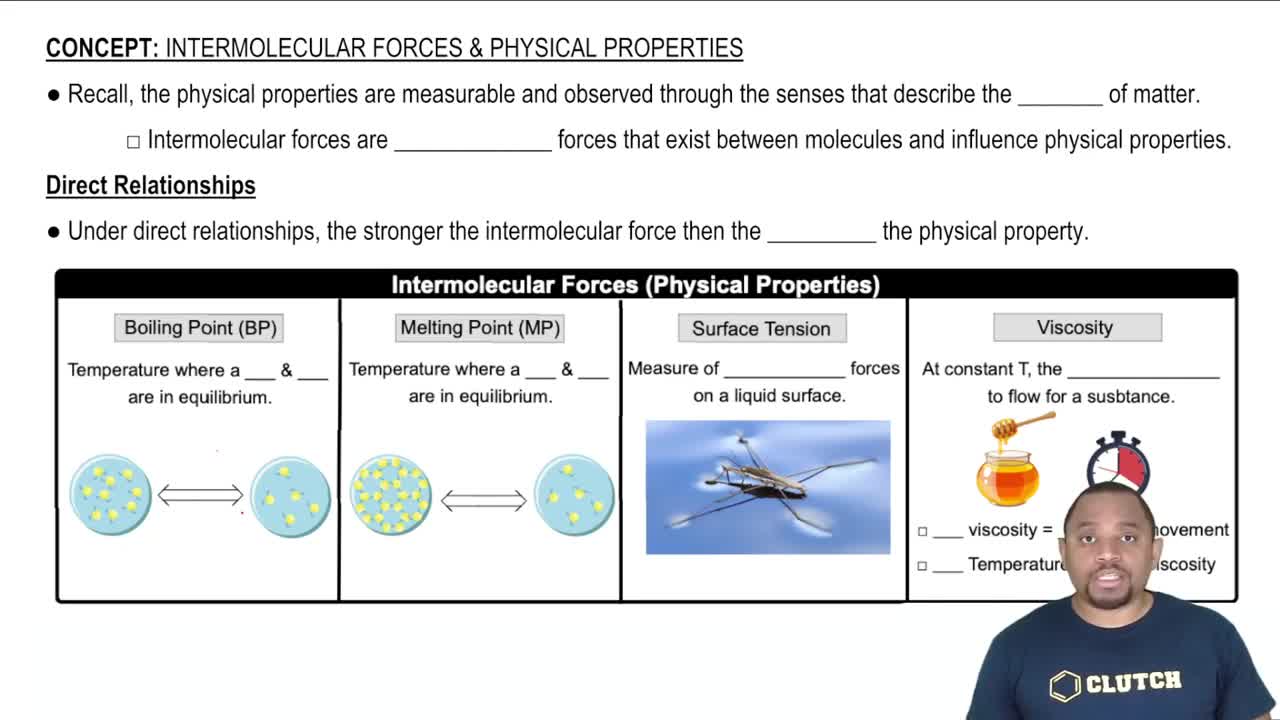
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is influenced by the interactions between molecules; higher viscosity indicates stronger intermolecular forces. In general, larger and more complex molecules, like those in olive oil, tend to have higher viscosities compared to smaller, simpler molecules like water.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Molecular Structure of Oleic Acid
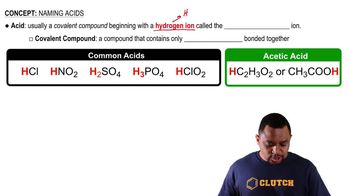
Oleic acid is a long-chain fatty acid with a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic carboxylic acid group. The long hydrocarbon chain contributes to its higher molecular weight and complexity, leading to increased van der Waals forces between molecules. This structural characteristic enhances the viscosity of olive oil compared to water, which has a simpler molecular structure.
Recommended video:
Acids and Their Structure
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules. In olive oil, the presence of long hydrocarbon chains leads to stronger London dispersion forces, while water primarily exhibits hydrogen bonding. The stronger intermolecular forces in olive oil result in a higher viscosity compared to the relatively weaker forces in water.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance