(b) An AB4 molecule has two lone pairs of electrons on the A atom (in addition to the four B atoms). What is the electron-domain geometry around the A atom?
Give the electron-domain and molecular geometries for the following molecules and ions: a. HCN
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
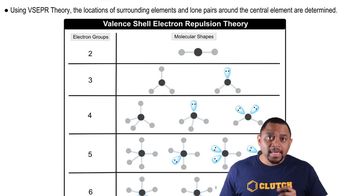
Key Concepts
Electron-Domain Geometry

Molecular Geometry

VSEPR Theory
Would you expect the nonbonding electron-pair domain in NH3 to be greater or less in size than the corresponding one in PH3?
In which of the following molecules can you confidently predict the bond angles about the central atom, and for which would you be a bit uncertain? Explain in each case. (a) H2S, (b) BCl3, (c) CH3I, (d) CBr4, (e) TeBr4.
Give the electron-domain and molecular geometries for the following molecules and ions: c. SF4
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following molecules or ions, and predict their electron-domain and molecular geometries: (e) XeF2
The figure that follows contains ball-and-stick drawings of three possible shapes of an AF4 molecule. (c) Which of the following elements will lead to an AF4 molecule with the shape in (iii): Be, C, S, Se, Si, Xe? i.
ii.
iii.
