Place the following pairs of elements in order from smallest to largest difference in electronegativity: K and F, S and O, Br and I, Ca and Se, Li and Cl.
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
Chapter 8, Problem 43
Which of the following bonds are polar: a. B —F, b. Cl — Cl, c. Se — O, d. H—I? Which is the more electronegative atom in each polar bond?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1> Determine the electronegativity of each atom in the bonds: B, F, Cl, Se, O, H, and I.
insert step 2> Compare the electronegativity values of the atoms in each bond to determine if there is a significant difference.
insert step 3> Identify the bonds with a significant difference in electronegativity as polar bonds.
insert step 4> For each polar bond, identify the atom with the higher electronegativity as the more electronegative atom.
insert step 5> List the polar bonds and the more electronegative atom in each.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. It varies across the periodic table, with elements like fluorine being highly electronegative. In a bond between two different atoms, the atom with higher electronegativity will attract the shared electrons more strongly, leading to a polar bond.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electronegativity Trends
Polar Bonds
A polar bond occurs when there is a significant difference in electronegativity between the two atoms involved in the bond. This difference causes an uneven distribution of electron density, resulting in a dipole moment where one end of the bond is slightly negative and the other slightly positive. Bonds such as B-F and Se-O are examples of polar bonds due to the differing electronegativities of the atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Polarity
Bond Types
Bonds can be classified as polar or nonpolar based on the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. Nonpolar bonds, like Cl-Cl, occur between identical atoms where electron sharing is equal. Understanding the type of bond helps predict molecular behavior, reactivity, and interactions with other molecules, which is crucial in chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course
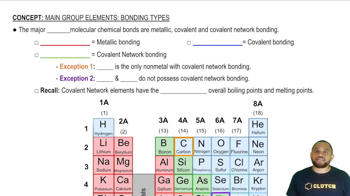
Bonding Types
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Using only the periodic table as your guide, select the most electronegative atom in each of the following sets: (d) Zn, Ge, Ga, As.
545
views
Textbook Question
By referring only to the periodic table, select (d) the element in the group K, C, Zn, F that is most likely to form an ionic compound with Ba.
591
views
Textbook Question
Arrange the bonds in each of the following sets in order of increasing polarity: (b) O—Cl,S—Br, C—P
1222
views
Textbook Question
Arrange the bonds in each of the following sets in order of increasing polarity: (c) C—S, B— F, N — O.
697
views
Textbook Question
(a) From the data in Table 8.2, calculate the effective charges on the H atom of the HBr molecule in units of the electronic charge, e.
2145
views
1
comments
