Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, typically measured from the nucleus to the outer boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons. In the periodic table, atomic radius generally increases down a group due to the addition of electron shells, while it decreases across a period from left to right due to increased nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
Recommended video:
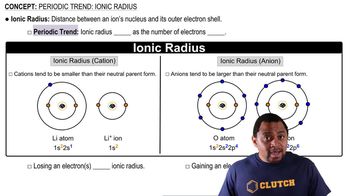
Ionic Radius
Ionic radius is the measure of an atom's ion in a crystal lattice. Cations (positively charged ions) are smaller than their neutral atoms because they lose an electron, reducing electron-electron repulsion and allowing the remaining electrons to be pulled closer to the nucleus. Conversely, anions (negatively charged ions) are larger than their neutral atoms due to the addition of electrons, which increases repulsion among them.
Recommended video:
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are patterns observed in the periodic table that illustrate how certain properties of elements change across periods and down groups. Key trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Understanding these trends helps predict the behavior of elements, such as the relative sizes of F, Br, and Br-, which can be inferred from their positions in the periodic table.
Recommended video: