Because the oxide ion is basic, metal oxides react readily with acids. (a) Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: FeO(s) + 2 HClO4(aq) → Fe(ClO4)2(aq) + H2O(l) (b) Based on the equation in part (a), write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs between NiO(s) and an aqueous solution of nitric acid.
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Chapter 4, Problem 48a,b,c
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (a) barium sulfate, BaSO4 (b) sulfurous acid, H2SO3 (c) strontium sulfide, SrS
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the general formula for sulfurous acid, which is \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_3 \).
Assign oxidation numbers to hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen typically has an oxidation number of +1, and oxygen typically has an oxidation number of -2.
Set up an equation based on the sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound, which should equal zero: \( 2(+1) + x + 3(-2) = 0 \), where \( x \) is the oxidation number of sulfur.
Simplify the equation: \( 2 + x - 6 = 0 \).
Solve for \( x \) to find the oxidation number of sulfur.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation Number
The oxidation number, or oxidation state, is a theoretical charge assigned to an atom in a compound based on the assumption that electrons are completely transferred. It helps in understanding the electron distribution in molecules and is crucial for identifying redox reactions. Oxidation numbers can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on the atom's electron gain or loss.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
There are specific rules for assigning oxidation numbers, such as the oxidation number of an element in its standard state is zero, and the sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound must equal zero. For hydrogen, the oxidation number is typically +1, while for oxygen, it is usually -2. These rules guide the determination of oxidation states in complex molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Number Rules
Structure of Sulfurous Acid (H2SO3)
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) consists of two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and three oxygen atoms. The sulfur atom is central to the molecule, bonded to one hydroxyl group (–OH) and two oxygen atoms, one of which is double-bonded. Understanding the molecular structure is essential for determining the oxidation state of sulfur, as it influences how electrons are shared or transferred in the compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course
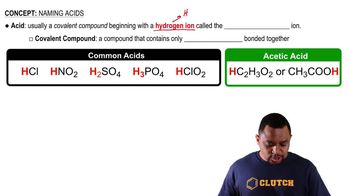
Acids and Their Structure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
508
views
Textbook Question
True or false: a. If a substance is oxidized, it is gaining electrons.
2
views
Textbook Question
(a) Which region of the periodic table shown here contains elements that are easiest to oxidize? (b) Which region contains the least readily oxidized elements?
1338
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (d) hydrogen sulfide, H2S
524
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (e) Locate sulfur in the periodic table in Exercise 4.47; what region is it in?
499
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (f) Which region(s) of the periodic table contains elements that can adopt both positive and negative oxidation numbers?
710
views
