Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
c. acetic acid and phenol.
Name the compound in each case.
 Brown 15th Edition
Brown 15th Edition Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Problem 47a
Problem 47a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
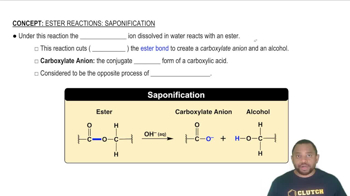


Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
c. acetic acid and phenol.
Name the compound in each case.
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
a. butanoic acid and methanol
Name the compound in each case.
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
b. benzoic acid and 2-propanol
Name the compound in each case.
Write a balanced chemical equation using condensed structural formulas for the saponification (base hydrolysis) of
b. phenyl acetate.
Write a balanced chemical equation using condensed structural formulas for
a. the formation of butyl propionate from the appropriate acid and alcohol
Write a balanced chemical equation using condensed structural formulas for
b. the saponification (base hydrolysis) of methyl benzoate.