Assume that 30.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base B that accepts one proton is titrated with a 0.10 M solution of the monoprotic strong acid HA. (b) What is the predominant form of B at the equivalence point?
How many milliliters of 0.105 M HCl are needed to titrate each of the following solutions to the equivalence point: (b) 22.5 mL of 0.118 M NH3?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Titration

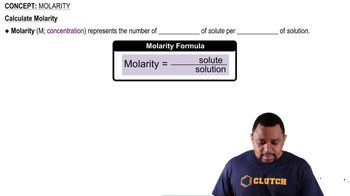
Molarity (M)
Neutralization Reaction

Assume that 30.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base B that accepts one proton is titrated with a 0.10 M solution of the monoprotic strong acid HA. (c) Is the pH 7, less than 7, or more than 7 at the equivalence point?
How many milliliters of 0.0850 M NaOH are required to titrate each of the following solutions to the equivalence point: (c) 50.0 mL of a solution that contains 1.85 g of HCl per liter?
A 20.0-mL sample of 0.200 M HBr solution is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of base have been added:
(b) 19.9 mL.
A 20.0-mL sample of 0.200 M HBr solution is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of base have been added:
(c) 20.0 mL.
A 20.0-mL sample of 0.200 M HBr solution is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of base have been added: (e) 35.0 mL.
