Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HCOOH, (ii) HPO42-.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 23a
The hydrogen sulfite ion 1HSO3-2 is amphiprotic. Write a balanced chemical equation showing how it acts as an acid toward water and another equation showing how it acts as a base toward water.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the amphiprotic nature of the hydrogen sulfite ion (HSO_3^-). It can donate a proton (H^+) acting as an acid, or accept a proton acting as a base.
To show HSO_3^- acting as an acid, write the chemical equation where it donates a proton to water (H_2O), forming bisulfite ion (SO_3^{2-}) and hydronium ion (H_3O^+).
The equation for HSO_3^- acting as an acid is: \[ \text{HSO}_3^- + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow \text{SO}_3^{2-} + \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \]
To show HSO_3^- acting as a base, write the chemical equation where it accepts a proton from water, forming sulfurous acid (H_2SO_3) and hydroxide ion (OH^-).
The equation for HSO_3^- acting as a base is: \[ \text{HSO}_3^- + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{SO}_3 + \text{OH}^- \]

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amphiprotic Species
An amphiprotic species is a substance that can both donate and accept protons (H+ ions). This dual capability allows it to act as an acid in some reactions and as a base in others. For example, the hydrogen sulfite ion (HSO3-) can donate a proton to water, forming bisulfite (SO3^2-) and hydronium (H3O+), or accept a proton from water, forming sulfuric acid (H2SO3) and hydroxide (OH-).
Recommended video:
Guided course
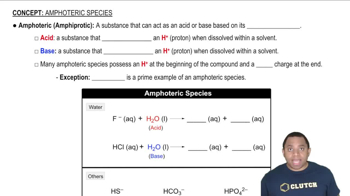
Amphoteric Species
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons between reactants. In these reactions, acids are proton donors, while bases are proton acceptors. Understanding this concept is crucial for writing balanced chemical equations, as it helps identify the products formed when an amphiprotic species interacts with water, either donating or accepting a proton.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Reaction
Balanced Chemical Equations
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Balancing ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld. When writing equations for the amphiprotic behavior of HSO3-, it is essential to account for all reactants and products, ensuring that the total number of atoms for each element remains constant.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
509
views
Textbook Question
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and the Brønsted–Lowry base on the left side of each of the following equations, and also identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base of each on the right side: (b) 1CH323N1aq2 + H2O1l2Δ1CH323NH +1aq2 + OH -1aq2
293
views
Textbook Question
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and the Brønsted– Lowry base on the left side of each equation, and also identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base of each on the right side. (a) HBrO1aq2 + H2O1l2ΔH3O+1aq2 + BrO-1aq2
362
views
Textbook Question
What is the conjugate acid of HSO3-? What is its conjugate base?
1062
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Write an equation for the reaction in which H2C6H7O5-1aq2 acts as a base in H2O1l2.
317
views
Textbook Question
Write an equation for the reaction in which H2C6H7O5-1aq2 acts as an acid in H2O1l2.
798
views
