Butyric acid is responsible for the foul smell of rancid butter. The pKa of butyric acid is 4.84. (a) Calculate the pKb for the butyrate ion.
The following observations are made about a diprotic acid H2A: (i) A 0.10 M solution of H2A has pH = 3.30. (ii) A 0.10 M solution of the salt NaHA is acidic. Which of the following could be the value of pKa2 for H2A: (i) 3.22, (ii) 5.30, (iii) 7.47, or (iv) 9.82?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Diprotic Acids

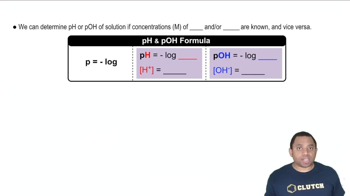
pH and pKa Relationship
Salt Hydrolysis

Butyric acid is responsible for the foul smell of rancid butter. The pKa of butyric acid is 4.84. (c) Calculate the pH of a 0.050 M solution of sodium butyrate.
Arrange the following 0.10 M solutions in order of increasing acidity: (i) NH4NO3, (ii) NaNO3, (iii) CH3COONH4, (iv) NaF, (v) CH3COONa.
The amino acid glycine (H2N–CH2–COOH) can participate in the following equilibria in water:
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O ⇌ H2N–CH2–COO– + H3O+ Ka = 4.3 × 10-3
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O⇌ +H3N–CH2–COOH + OH- Kb = 6.0 × 10-5
(a) Use the values of Ka and Kb to estimate the equilibrium constant for the intramolecular proton transfer to form a zwitterion: H2N–CH2–COOH ⇌ +H3N–CH2–COO–
The amino acid glycine (H2N–CH2–COOH) can participate in the following equilibria in water:
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O ⇌ H2N–CH2–COO– + H3O+ Ka = 4.3 × 10-3
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O⇌ +H3N–CH2–COOH + OH- Kb = 6.0 × 10-5
(b) What is the pH of a 0.050 M aqueous solution of glycine?
