The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of molecular iodine, I2(𝑔) ⇌ 2 I(𝑔), at 800 K is 𝐾𝑐 = 3.1×10−5. (b) Assuming both forward and reverse reactions are elementary reactions, which reaction has the larger rate constant, the forward or the reverse reaction?
Write the expressions for 𝐾𝑐 for the following reactions. In each case indicate whether the reaction is homogeneous or heterogeneous. (g) 2 C8H18(𝑙) + 25 O2(𝑔) ⇌ 16 CO2(𝑔) + 18 H2O(𝑙)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Equilibrium Constant (Kc)

Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Reactions
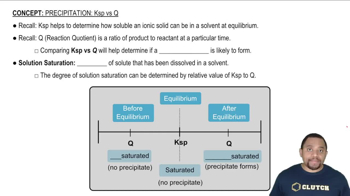
Phase Representation in Kc Expressions

Write the expression for 𝐾𝑐 for the following reactions. In each case indicate whether the reaction is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
(e) 2Ag(𝑠) + Zn2+(𝑎𝑞) ⇌ 2 Ag+(𝑎𝑞) + Zn(𝑠)
Write the expressions for 𝐾𝑐 for the following reactions. In each case indicate whether the reaction is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
(b) Ti(𝑠) + 2Cl2(𝑔) ⇌ TiCl4(𝑙)
Which of the following reactions lies to the right, favoring the formation of products, and which lies to the left, favoring the formation of reactants? (b) 2 HBr(𝑔) ⇌ H2(𝑔) + Br2(𝑔) 𝐾𝑐 = 5.8×10−18
Which of the following statements are true and which are false? (c) As the value of the equilibrium constant increases, the speed at which a reaction reaches equilibrium must increase.
If 𝐾𝑐 = 0.042 for PCl3(𝑔) + Cl2(𝑔) ⇌ PCl5(𝑔) at 500 K, what is the value of 𝐾𝑝 for this reaction at this temperature?
