Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They use dots to represent valence electrons and lines to represent bonds between atoms. Understanding how to draw and interpret Lewis structures is essential for determining the molecular geometry and reactivity of compounds.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
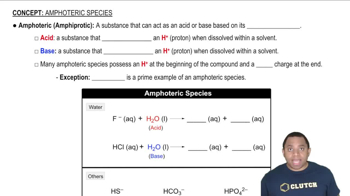
Molecular Charge
The molecular charge refers to the overall charge of a molecule or ion, which can be neutral, positive, or negative. It is determined by the difference between the number of protons (positively charged) and electrons (negatively charged) in the structure. Identifying whether a Lewis structure represents a neutral molecule or an ion involves counting the total valence electrons and comparing it to the expected number based on the constituent atoms.
Recommended video:
Ionic vs. Neutral Species
Ionic species are charged entities that result from the loss or gain of electrons, while neutral species have an equal number of protons and electrons. In the context of Lewis structures, recognizing whether a structure depicts an ion or a neutral molecule is crucial for understanding its chemical behavior and properties. The charge of an ion can often be inferred from the number of electrons depicted in the Lewis structure compared to the number of valence electrons expected for the atoms involved.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance