Acetylene 1C2H22 and nitrogen 1N22 both contain a triple bond, but they differ greatly in their chemical properties. (c) Write balanced chemical equations for the complete oxidation of N2 to form N2O51g2 and of acetylene to form CO21g2 and H2O1g2. Write a balanced chemical equation for the complete oxidation of acetylene to form CO2( g) and H2O(g).
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
Chapter 8, Problem 2b
Illustrated are four ions — A, B, X, and Y— showing their relative ionic radii. The ions shown in red carry positive charges: a 2+ charge for A and a 1+ charge for B. Ions shown in blue carry negative charges: a 1- charge for X and a 2- charge for Y. (b) Among the combinations in part (a), which leads to the ionic compound having the largest lattice energy?

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Radius
Ionic radius refers to the size of an ion in a crystal lattice. Cations (positively charged ions) are generally smaller than their parent atoms due to the loss of electrons, which reduces electron-electron repulsion. Conversely, anions (negatively charged ions) are larger because they gain electrons, increasing repulsion among them. Understanding ionic radii is crucial for predicting the stability and properties of ionic compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
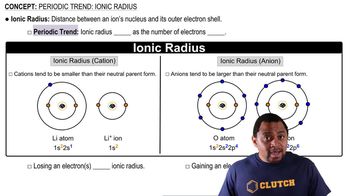
Ionic Radius
Lattice Energy
Lattice energy is the energy released when gaseous ions combine to form an ionic solid. It is a measure of the strength of the forces between the ions in an ionic compound. Larger charges and smaller ionic radii typically result in higher lattice energy, as the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions increases. This concept is essential for determining the stability and solubility of ionic compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lattice Energy
Charge Density
Charge density is defined as the charge of an ion divided by its volume, which is influenced by its ionic radius. Higher charge density indicates a stronger electrostatic attraction between ions, leading to greater lattice energy. In the context of ionic compounds, ions with higher charges and smaller radii will have higher charge densities, significantly affecting the overall stability and properties of the resulting compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Density Concepts
Related Practice
Textbook Question
350
views
Textbook Question
For each of these Lewis symbols, indicate the group in the periodic table in which the element X belongs: (a)
1644
views
Textbook Question
A portion of a two-dimensional 'slab' of NaCl(s) is shown here (see Figure 8.2) in which the ions are numbered. (a) Which colored balls must represent sodium ions?
516
views
Textbook Question
A portion of a two-dimensional 'slab' of NaCl(s) is shown here (see Figure 8.2) in which the ions are numbered. (d) Consider ion 5. How many repulsive interactions are shown for it?
513
views
Textbook Question
The orbital diagram that follows shows the valence electrons for a 2+ ion of an element. (a) What is the element?
1039
views
