Textbook Question
Discussing this chapter, a classmate says, 'Since elements that form cations are metals and elements that form anions are nonmetals, elements that do not form ions are metalloids.' Do you agree or disagree?
693
views
1
comments
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Discussing this chapter, a classmate says, 'Since elements that form cations are metals and elements that form anions are nonmetals, elements that do not form ions are metalloids.' Do you agree or disagree?
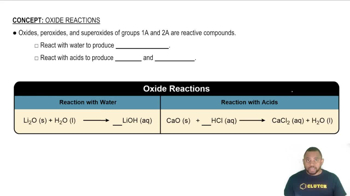
Predict whether each of the following oxides is ionic or molecular: SnO2, Al2O3, CO2, Li2O, Fe2O3, H2O.
Would you expect zirconium(II) oxide, ZrO, to react more readily with HCl(aq) or NaOH(aq)?
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (a) What is the name of this product (see Table 2.6)?
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (b) Write a balanced equation for the formation of Cl2O71l2 from the elements.
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (c) Would you expect Cl2O7 to be more reactive toward H+1aq2 or OH-1aq2?