Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (a) What is the name of this product (see Table 2.6)?
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
Chapter 7, Problem 64a
An element X reacts with oxygen to form XO2 and with chlorine to form XCl4. XO2 is a white solid that melts at high temperatures (above 1000 °C). Under usual conditions, XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 58 °C. (a) XCl4 reacts with water to form XO2 and another product. What is the likely identity of the other product?

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of reactants into products through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. In this case, the reaction of XCl4 with water illustrates a hydrolysis reaction, where water reacts with a compound to produce new substances, including an oxide and an acid or another product.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Properties
Oxides and Halides
Oxides are compounds formed by the reaction of an element with oxygen, while halides are compounds formed with halogens like chlorine. The question indicates that X forms XO2 (an oxide) and XCl4 (a halide), which suggests that X is likely a non-metal that can form stable compounds with both oxygen and chlorine.
Recommended video:
Guided course
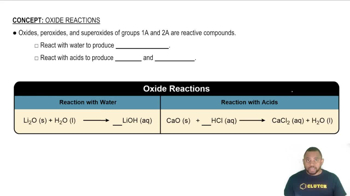
Oxide Reactions
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+) between reactants. In the context of the reaction between XCl4 and water, the likely other product is an acid formed from the chlorine component, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), indicating that XCl4 acts as a Lewis acid in this reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Reaction
Related Practice
Textbook Question
3662
views
Textbook Question
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (b) Write a balanced equation for the formation of Cl2O71l2 from the elements.
1585
views
Textbook Question
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (c) Would you expect Cl2O7 to be more reactive toward H+1aq2 or OH-1aq2?
543
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
An element X reacts with oxygen to form XO2 and with chlorine to form XCl4. XO2 is a white solid that melts at high temperatures (above 1000 °C). Under usual conditions, XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 58 °C. (b) Do you think that element X is a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid?
323
views
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the following reactions: (a) boron trichloride with water
357
views
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the following reactions: (d) arsenic trioxide with aqueous potassium hydroxide.
348
views
