(a) Is the number of moles of ions present in a solution an intensive or an extensive property?
(c) How many milliliters of a 6.00 M NaOH solution are needed to provide 0.350 mol of NaOH?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
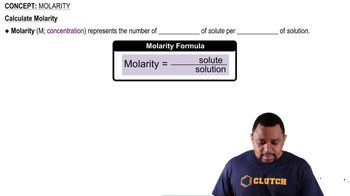
Molarity (M)
Stoichiometry

Volume Calculation

(b) Can you identify which one between 0.10 mol ZnCl2 and 0.1M ZnCl2 contains more Zn2+ ion? Why?
You make 1.000 L of an aqueous solution that contains 35.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11). (b) How many liters of water would you have to add to this solution to reduce the molarity you calculated in part (a) by a factor of two?
(b) How many moles of KBr are present in 150 mL of a 0.112 M solution?
(c) How many milliliters of 6.1 M HCl solution are needed to obtain 0.150 mol of HCl?
A person suffering from hyponatremia has a sodium ion concentration in the blood of 0.118 M and a total blood volume of 4.6 L. What mass of sodium chloride would need to be added to the blood to bring the sodium ion concentration up to 0.138 M, assuming no change in blood volume?
