Textbook Question
Give the name or condensed structural formula, as appropriate (e)
111
views
 Brown 14th Edition
Brown 14th Edition Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
Ch.24 - The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry Problem 43
Problem 43 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


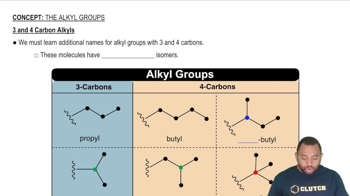
Give the name or condensed structural formula, as appropriate (e)
Describe the intermediate that is thought to form in the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene, using cyclohexene as the alkene in your description.
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
a. benzoic acid and ethanol
Name the compound in each case.
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
c. acetic acid and phenol.
Name the compound in each case.
Draw the condensed structure of the compounds formed by condensation reactions between
a. butanoic acid and methanol
Name the compound in each case.