How many of the indicated atoms are represented by each chemical formula: (a) carbon atoms in C4H9COOCH3
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
Chapter 2, Problem 54
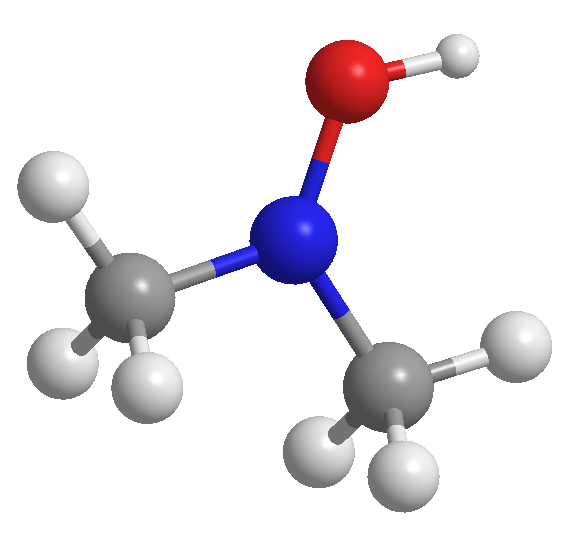
Write the molecular and structural formulas for the compounds represented by the following models:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the atoms in the model: The model contains carbon (gray), hydrogen (white), nitrogen (blue), and oxygen (red) atoms.
Count the number of each type of atom: There are 2 carbon atoms, 5 hydrogen atoms, 1 nitrogen atom, and 1 oxygen atom.
Determine the molecular formula: Combine the counts of each type of atom to form the molecular formula.
Analyze the structure: Identify the connectivity of the atoms. The nitrogen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms, one of which is bonded to an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom.
Write the structural formula: Based on the connectivity, draw the structural formula showing the arrangement of atoms and bonds.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Formula
The molecular formula of a compound indicates the number and types of atoms present in a molecule. It is expressed using chemical symbols and subscripts, where each symbol represents an element and the subscript denotes the number of atoms of that element. For example, the molecular formula C2H6O indicates a molecule containing two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Determining Molecular Formulas
Structural Formula
The structural formula provides a visual representation of the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how atoms are bonded to each other. It can depict single, double, or triple bonds and may include information about the geometry of the molecule. This is crucial for understanding the compound's reactivity and properties, as the arrangement of atoms affects how the molecule interacts with others.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Structural Formula
Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding refers to the forces that hold atoms together in a molecule. The main types of bonds include covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons, and ionic bonds, where electrons are transferred between atoms. Understanding the type of bonding in a compound is essential for predicting its behavior, stability, and reactivity, as well as for deriving its molecular and structural formulas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Bonds
Related Practice
Textbook Question
551
views
Textbook Question
How many of the indicated atoms are represented by each chemical formula: (b) oxygen atoms in Ca(ClO3)2 (c) hydrogen atoms in (NH4)2HPO4?
533
views
Textbook Question
Write the molecular and structural formulas for the compounds represented by the following molecular models:
909
views
Textbook Question
Fill in the gaps in the following table: Symbol 59Co3+ Protons 34 76 80 Neutrons 46 116 120 Electrons 36 78 Net charge 2+
1573
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
Fill in the gaps in the following table: Symbol 133Cs+ Protons 35 15 Neutrons 46 16 30 Electrons 18 20 Net charge 1- 5+
720
views
Textbook Question
Each of the following elements is capable of forming an ion in chemical reactions. By referring to the periodic table, predict the charge of the most stable ion of each: (a) Be (b) Rb (c) As (d) In (e) At.
682
views
