An unknown particle is caused to move between two electrically charged plates, as illustrated in Figure 2.7. You hypothesize that the particle is a proton. (a) If your hypothesis is correct, would the particle be deflected in the same or opposite direction as the b rays?
Millikan determined the charge on the electron by studying the static charges on oil drops falling in an electric field (Figure 2.5). A student carried out this experiment using several oil drops for her measurements and calculated the charges on the drops. She obtained the following data: Droplet Calculated Charge (C) A 1.60 * 10-19 B 3.15 * 10-19 C 4.81 * 10-19 D 6.31 * 10-19 (b) What conclusion can the student draw from these data regarding the charge of the electron?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment
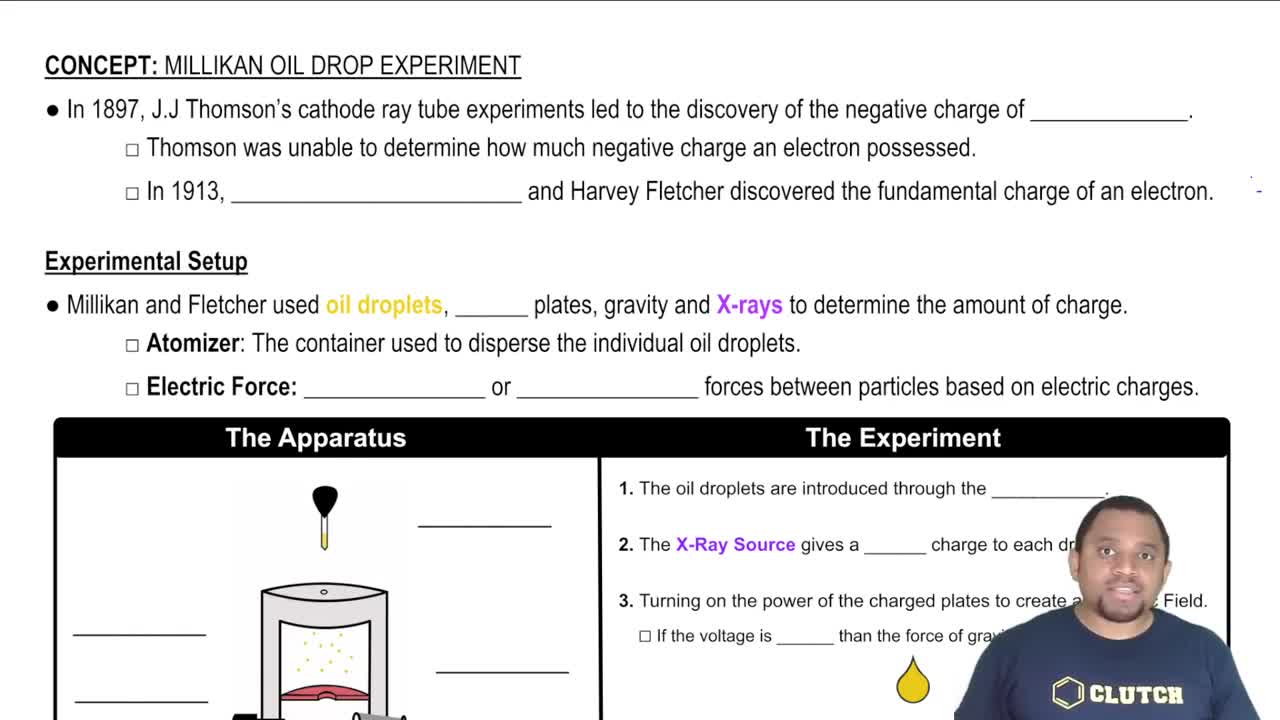
Quantization of Charge

Data Analysis and Conclusion Drawing

An unknown particle is caused to move between two electrically charged plates, as illustrated in Figure 2.7. You hypothesize that the particle is a proton. (b) Would it be deflected by a smaller or larger amount than the b rays?
Millikan determined the charge on the electron by studying the static charges on oil drops falling in an electric field (Figure 2.5). A student carried out this experiment using several oil drops for her measurements and calculated the charges on the drops. She obtained the following data: Droplet Calculated Charge (C) A 1.60 * 10-19 B 3.15 * 10-19 C 4.81 * 10-19 D 6.31 * 10-19 (c) What value (and to how many significant figures) should she report for the electronic charge?
The radius of an atom of tungsten (W) is about 2.10 A . (c) If the atom is assumed to be a sphere, what is the volume in m3 of a single W atom?
The radius of an atom of copper (Cu) is about 140 pm. (c) If you assume that the Cu atom is a sphere, what is the volume in cm3 of a single atom?
