Massspectrometry is more often applied to molecules than to atoms. We will see in Chapter 3 that the molecular weight of a molecule is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in the molecule. The mass spectrum of H2 is taken under conditions that prevent decomposition into H atoms. The two naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen are 1H (atomic mass = 1.00783 amu; abundance 99.9885%) and 2H (atomic mass = 2.01410; abundance 0.0115%). (a) How many peaks will the mass spectrum have?
For each of the following elements, write its chemical symbol, determine the name of the group to which it belongs (Table 2.3), and indicate whether it is a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal: (e) sulfur.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
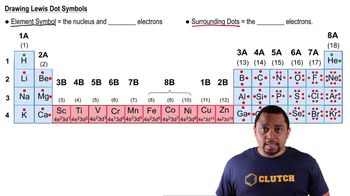
Chemical Symbols
Periodic Table Groups
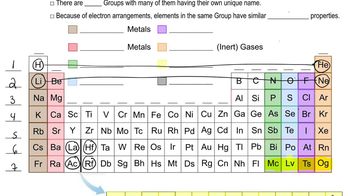
Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals

Massspectrometry is more often applied to molecules than to atoms. We will see in Chapter 3 that the molecular weight of a molecule is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in the molecule. The mass spectrum of H2 is taken under conditions that prevent decomposition into H atoms. The two naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen are 1H (atomic mass = 1.00783 amu; abundance 99.9885%) and 2H (atomic mass = 2.01410; abundance 0.0115%). (c) Which peak will be the largest, and which the smallest?
For each of the following elements, write its chemical symbol, locate it in the periodic table, give its atomic number, and indicate whether it is a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal: (g) arsenic.
The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (b) Determine the empirical formula of each.
The structural formulas of the compounds n-butane and isobutane are shown below. (c) Which formulas—empirical, molecular, or structural—allow you determine these are different compounds?
Ball-and-stick representations of benzene, a colorless liquid often used in organic chemistry reactions, and acetylene, a gas used as a fuel for high-temperature welding, are shown below. (a) Determine the molecular formula of each.
