The beaker on the right contains 0.1 M acetic acid solution with methyl orange as an indicator. The beaker on the left contains a mixture of 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.1 M sodium acetate with methyl orange. (b) Which solution is better able to maintain its pH when small amounts of NaOH are added? Explain. [Sections 17.1 and 17.2]
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria
Chapter 17, Problem 2a
The beaker on the right contains 0.1 M acetic acid solution with methyl orange as an indicator. The beaker on the left contains a mixture of 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.1 M sodium acetate with methyl orange. (a) Using Figures 16.8 and 16.9, which solution has a higher pH?

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Chemistry
Acid-base chemistry involves the study of acids, bases, and their reactions. Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions), while bases accept protons. The strength of an acid or base is often measured by its dissociation in water, which affects the pH of the solution. Understanding the properties of weak acids like acetic acid and their conjugate bases is crucial for predicting pH changes in solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Buffer Solutions
A buffer solution is a system that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base, which can neutralize added acids or bases. In this case, the mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts as a buffer, maintaining a relatively stable pH compared to the acetic acid solution alone, which is more susceptible to pH changes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Solutions
pH and Indicators
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, with lower values indicating higher acidity. Indicators like methyl orange change color at specific pH ranges, providing visual cues about the solution's acidity. Understanding how the pH of a solution affects the color change of an indicator is essential for interpreting the results of acid-base reactions and determining which solution has a higher pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
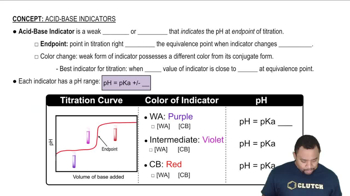
Acid-Base Indicators
Related Practice
Textbook Question
642
views
Textbook Question
A buffer contains a weak acid, HA, and its conjugate base. The weak acid has a pKa of 4.5, and the buffer has a pH of 4.3. Without doing a calculation, state which of these possibilities are correct at pH 4.3. (a) 3HA4 = 3A-4, (b) 3HA4 7 3A-4, or (c) 3HA4 6 3A-4. [Section 17.2]
2791
views
Textbook Question
The following diagram represents a buffer composed of equal concentrations of a weak acid, HA, and its conjugate base, A-. The heights of the columns are proportional to the concentrations of the components of the buffer. (a) Which of the three drawings, (1), (2), or (3), represents the buffer after the addition of a strong acid? [Section 17.2]
377
views
