Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Titration
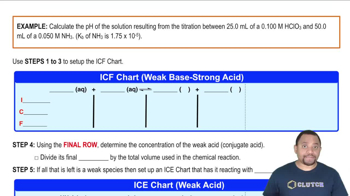
An acid-base titration is a quantitative analytical method used to determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution. During the titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of unknown concentration until the reaction reaches its equivalence point, where the amount of acid equals the amount of base. The pH at this point can vary depending on the nature of the acid and base involved.
Recommended video:
Equivalence Point and pH
The equivalence point in a titration is the stage at which the number of moles of titrant equals the number of moles of the substance being titrated. The pH at the equivalence point is influenced by the strength of the acid and base. For strong acid-strong base titrations, the pH is typically 7, while for weak acid-strong base titrations, the pH is above 7, and for strong acid-weak base titrations, it is below 7.
Recommended video:
pH at the Equivalence Point Example
Weak Acid Behavior
Formic acid is a weak acid, meaning it does not completely dissociate in solution. When titrated with a strong base like NaOH, the resulting solution at the equivalence point will contain the conjugate base of the weak acid, which can hydrolyze to produce hydroxide ions, leading to a pH greater than 7. This behavior is crucial for predicting the pH at the equivalence point in titrations involving weak acids.
Recommended video: