Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility of LaF3 in grams per liter in (c) 0.050 M LaCl3 solution.
487
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

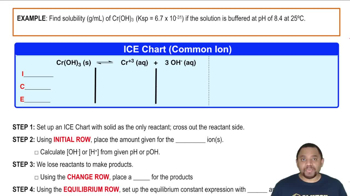

Calculate the solubility of LaF3 in grams per liter in (c) 0.050 M LaCl3 solution.
Consider a beaker containing a saturated solution of CaF2 in equilibrium with undissolved CaF21s2. Solid CaCl2 is then added to the solution. (a) Will the amount of solid CaF2 at the bottom of the beaker increase, decrease, or remain the same?
Calculate the solubility of Mn1OH22 in grams per liter when buffered at pH (b) 9.5.
Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (b) 10.0.
Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (c) 12.0.