Label each of the following as being a strong base, a weak base, or a species with negligible basicity. In each case write the formula of its conjugate acid, and indicate whether the conjugate acid is a strong acid, a weak acid, or a species with negligible acidity: (d) Cl-
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 23
Which of the following is the stronger Brønsted–Lowry acid, HBrO or HBr?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid concept: A Brønsted–Lowry acid is a substance that donates a proton (H⁺) in a chemical reaction.
Consider the molecular structure and bond strength: HBr is a binary acid, while HBrO is an oxyacid. Binary acids like HBr typically have stronger acidic properties due to the weaker H-Br bond compared to the H-O bond in HBrO.
Evaluate the electronegativity and stability of the conjugate base: The conjugate base of HBr is Br⁻, which is more stable than the conjugate base of HBrO, BrO⁻, due to the lack of additional electronegative atoms that can stabilize the negative charge.
Consider the acid dissociation constant (Ka): Generally, a higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid. HBr, being a strong acid, completely dissociates in water, while HBrO is a weak acid with a lower Ka value.
Conclude based on the above analysis: HBr is the stronger Brønsted–Lowry acid compared to HBrO due to its complete dissociation and the stability of its conjugate base.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
57sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Brønsted–Lowry Acid-Base Theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. This framework allows for the classification of substances based on their ability to donate or accept protons in a chemical reaction. Understanding this theory is essential for determining the strength of acids and bases in various contexts.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
Acid Strength
Acid strength refers to the ability of an acid to donate protons in solution. Stronger acids dissociate more completely in water, releasing more protons, while weaker acids do not dissociate as fully. The strength of an acid can be compared using its dissociation constant (Ka), with larger values indicating stronger acids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
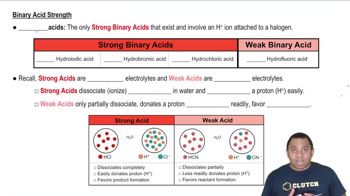
Binary Acid Strengths
Comparative Analysis of Acids
To determine which acid is stronger between HBrO and HBr, one must compare their dissociation in water. HBr is a strong acid that completely dissociates, while HBrO is a weak acid that does not dissociate fully. This comparative analysis is crucial for identifying the stronger acid based on their behavior in aqueous solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Comparing Binary Acid Strength
Related Practice
Textbook Question
273
views
Textbook Question
Label each of the following as being a strong base, a weak base, or a species with negligible basicity. In each case write the formula of its conjugate acid, and indicate whether the conjugate acid is a strong acid, a weak acid, or a species with negligible acidity: (e) NH3.
334
views
Textbook Question
Label each of the following as being a strong acid, a weak
acid, or a species with negligible acidity. In each case write the
formula of its conjugate base, and indicate whether the conjugate
base is a strong base, a weak base, or a species with negligible
basicity: (a) HCOOH
295
views
Open Question
Which of the following is the stronger Brønsted–Lowry acid, HClO3 or HClO2?
Textbook Question
Predict the products of the following acid–base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow:
(a) O2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌
(b) CH3COOH(aq) + HS-(aq) ⇌
(c) NO2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌
990
views
Textbook Question
Predict the products of the following acid–base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow:
(a) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌
(b) CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+(aq) ⇌
(c) HCO3-(aq) + F-(aq) ⇌
983
views
