Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HCOOH, (ii) HPO42-.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria
Chapter 16, Problem 18a
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and the Brønsted– Lowry base on the left side of each equation, and also identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base of each on the right side. (a) HBrO1aq2 + H2O1l2ΔH3O+1aq2 + BrO-1aq2

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Brønsted–Lowry Acid-Base Theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. This framework emphasizes the transfer of protons (H⁺ ions) during chemical reactions, allowing for a broader understanding of acid-base behavior beyond just the presence of hydroxide or hydronium ions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
In the Brønsted–Lowry theory, a conjugate acid is formed when a base gains a proton, while a conjugate base is what remains after an acid donates a proton. This relationship highlights the reversible nature of acid-base reactions, where the products can act as acids or bases in subsequent reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Identifying Species in Reactions
To analyze acid-base reactions, it is essential to identify the reactants and products correctly. In the given equation, recognizing which species donate or accept protons allows for the determination of the Brønsted–Lowry acid and base, as well as their corresponding conjugate pairs, facilitating a deeper understanding of the reaction dynamics.
Recommended video:
Guided course
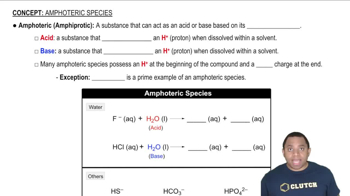
Amphoteric Species
Related Practice
Textbook Question
509
views
Textbook Question
Give the conjugate acid of the following Brønsted–Lowry bases: (i) SO42-, (ii) CH3NH2.
535
views
Textbook Question
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and the Brønsted–Lowry base on the left side of each of the following equations, and also identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base of each on the right side: (b) 1CH323N1aq2 + H2O1l2Δ1CH323NH +1aq2 + OH -1aq2
293
views
Textbook Question
The hydrogen sulfite ion 1HSO3-2 is amphiprotic. Write a balanced chemical equation showing how it acts as an acid toward water and another equation showing how it acts as a base toward water.
1346
views
Textbook Question
What is the conjugate acid of HSO3-? What is its conjugate base?
1062
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Write an equation for the reaction in which H2C6H7O5-1aq2 acts as a base in H2O1l2.
317
views
