Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Principles
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. Water solubility is influenced by the presence of polar functional groups, which interact favorably with water molecules, while fat solubility is associated with nonpolar characteristics that dissolve in lipids. Understanding these principles helps predict how vitamins behave in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Uncertainty Principle Formula
Chemical Structure of Vitamins
The chemical structure of vitamins, including the presence of functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) or carboxyl (-COOH), plays a crucial role in determining their solubility. For instance, vitamins with more hydrophilic groups tend to be more water-soluble, while those with long hydrocarbon chains are typically more fat-soluble. Analyzing the structures of vitamins E and B6 is essential for making solubility predictions.
Recommended video:
Hydrophilic vs. Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic substances are attracted to water and tend to dissolve in it, while hydrophobic substances repel water and are more soluble in fats. This distinction is vital when predicting the solubility of vitamins, as it directly relates to their functional roles in the body. Recognizing which vitamin has hydrophilic or hydrophobic characteristics aids in understanding their absorption and transport mechanisms.
Recommended video:
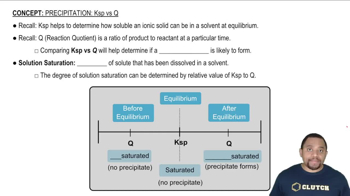
Ksp vs Q in Precipitation