What is the molarity of each of the following solutions: (b) 5.25 g of Mn(NO3)2⋅2H2O in 175 mL of solution,
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a water-soluble vitamin. A solution containing 80.5 g of ascorbic acid dissolved in 210 g of water has a density of 1.22 g/mL at 55 °C. Calculate (c) the molality,

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Molality

Moles of Solute
Density and Volume Relationship

Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a water-soluble vitamin. A solution containing 80.5 g of ascorbic acid dissolved in 210 g of water has a density of 1.22 g/mL at 55 °C. Calculate (a) the mass percentage,
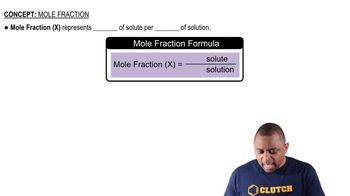
The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (a) What is the mole fraction of methanol in the solution?
The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (b) What is the molality of the solution?
The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (c) Assuming that the volumes are additive, what is the molarity of CH3OH in the solution?
