The phase diagram of a hypothetical substance is
(b) What is the physical state of the substance under the following conditions? (i) T = 150 K, P = 0.2 atm; (ii) T = 100 K, P = 0.8 atm; (iii) T = 300K, P = 1.0atm. [Section 11.6]
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Phase Diagrams
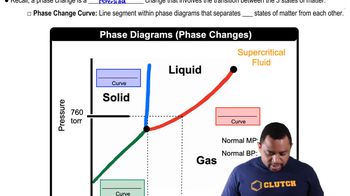
Critical Point

Triple Point

Using this graph of CS2 data, determine (a) the approximate vapor pressure of CS2 at 30°C,
The molecules
have the same molecular formula (C3H8O) but different chemical structures. (b) Which molecule do you expect to have a larger dipole moment? [Sections 11.2 and 11.5]
At three different temperatures, T1, T2, and T3, the molecules in a liquid crystal align in these ways:
(a) At which temperature or temperatures is the substance in a liquid crystalline state? At those temperatures, which type of liquid crystalline phase is depicted?
At three different temperatures, T1, T2, and T3, the molecules in a liquid crystal align in these ways:
(b) Which is the highest of these three temperatures? [Section 11.7]
List the three states of matter in order of (a) increasing molecular disorder
