An open-end manometer containing mercury is connected to a container of gas, as depicted in Sample Exercise 10.2. What is the pressure of the enclosed gas in torr in each of the following situations? (a) The mercury in the arm attached to the gas is 15.4 mm higher than in the one open to the atmosphere; atmospheric pressure is 0.985 atm.
Ch.10 - Gases
Chapter 10, Problem 27a
(a) Amonton's law expresses the relationship between pressure and temperature. Use Charles's law and Boyle's law to derive the proportionality relationship between P and T.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by recalling Charles's Law, which states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant pressure: \( V \propto T \) or \( V = kT \), where \( k \) is a constant.
Recall Boyle's Law, which states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature: \( P \propto \frac{1}{V} \) or \( PV = k' \), where \( k' \) is a constant.
Combine the two laws by substituting the expression for \( V \) from Charles's Law into Boyle's Law: \( P(kT) = k' \).
Simplify the equation to express the relationship between pressure and temperature: \( P \propto T \) or \( P = k''T \), where \( k'' \) is a new constant.
Conclude that Amonton's Law, which is also known as Gay-Lussac's Law, states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when volume is held constant.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amonton's Law
Amonton's Law, also known as the pressure-temperature law, states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when the volume is held constant. This relationship implies that as the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules increases, leading to higher pressure if the volume does not change.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Hess's Law
Charles's Law
Charles's Law describes how the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature when pressure is held constant. This means that if the temperature of a gas increases, its volume will also increase, provided the pressure remains unchanged. This law is essential for understanding how temperature affects gas behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course
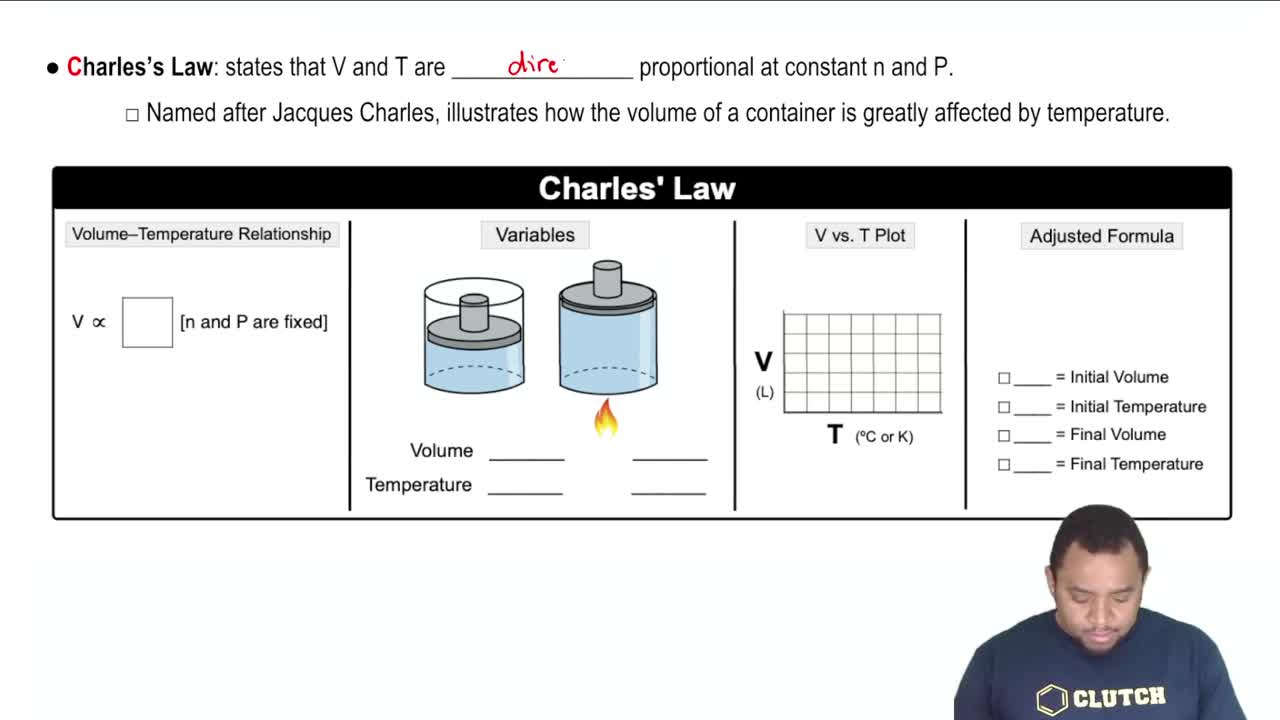
Charles's Law
Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when the temperature is held constant. This means that if the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases, assuming the temperature remains constant. This law is crucial for analyzing the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature in gas systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Boyle's Law
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1014
views
Textbook Question
You have a gas at 25 C confined to a cylinder with a movable piston. Which of the following actions would double the gas pressure? (a) Lifting up on the piston to double the volume while keeping the temperature constant (b) Heating the gas so that its temperature rises from 25 C to 50 C, while keeping the volume constant (c) Pushing down on the piston to halve the volume while keeping the temperature constant.
962
views
Open Question
A fixed quantity of gas at 25 _x001F_C exhibits a pressure of 99 kPa and occupies a volume of 4.00 L. (a) Calculate the volume the gas will occupy if the pressure is increased to 202.6 kPa while the temperature is held constant. (b) Calculate the volume the gas will occupy if the temperature is increased to 100 °C while the pressure is held constant.
Textbook Question
(b) If a car tire is filled to a pressure of 220.6 kPa measured at 24 °C, what will be the tire pressure if the tires heat up to 49 °C during driving?
1335
views
Open Question
In the contact process, sulfur dioxide and oxygen gas react to form sulfur trioxide as follows: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g). At a certain temperature and pressure, 50 L of SO2 reacts with 25 L of O2. If all the SO2 and O2 are consumed, what volume of SO3, at the same temperature and pressure, will be produced?
Textbook Question
(b) What is the molar volume of an ideal gas at STP?
803
views
