MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
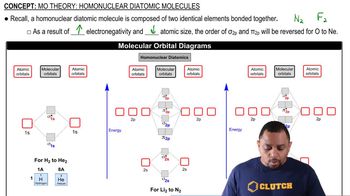
- Homonuclear Diatomic MoleculesMolecules composed of two identical atoms, such as N2 or F2, with unique molecular orbital structures.
- Molecular Orbital DiagramsVisual representations of molecular orbitals showing the distribution of electrons in homonuclear diatomic molecules.
- Valence ElectronsElectrons in the outermost shell of an atom, crucial for bonding and molecular orbital formation.
- 1s OrbitalThe lowest energy atomic orbital, occupied by valence electrons in period 1 elements like hydrogen and helium.
- σ1sA bonding molecular orbital formed from the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals in diatomic molecules.
- σ*1sAn antibonding molecular orbital formed from the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals in diatomic molecules.
- 2s OrbitalAn atomic orbital in period 2 elements, involved in forming molecular orbitals in diatomic molecules.
- σ2sA bonding molecular orbital formed from the overlap of 2s atomic orbitals in period 2 diatomic molecules.
- σ*2sAn antibonding molecular orbital formed from the overlap of 2s atomic orbitals in period 2 diatomic molecules.
- 2p OrbitalAn atomic orbital in period 2 elements, contributing to complex molecular orbital structures.
- π2pA bonding molecular orbital formed from the side-by-side overlap of 2p atomic orbitals.
- π*2pAn antibonding molecular orbital formed from the side-by-side overlap of 2p atomic orbitals.
- ElectronegativityA measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons, affecting molecular orbital order in diatomic molecules.
- Atomic SizeThe size of an atom, influencing the order of molecular orbitals in diatomic molecules.
- Period 2 ElementsElements from lithium to neon, with complex molecular orbital arrangements in diatomic molecules.