Energy Diagrams definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEnergy Diagrams definitions
1/13
Terms in this set (13)
- Energy DiagramA graph illustrating the energy changes of reactants, products, and transition state during a chemical reaction.
- ReactantsSubstances present at the start of a chemical reaction, located on the left side of an energy diagram.
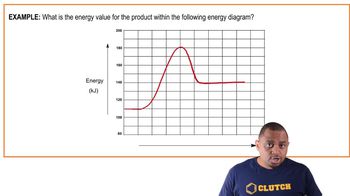
- ProductsSubstances formed at the end of a chemical reaction, located on the right side of an energy diagram.
- Transition StateThe highest energy structure along the reaction coordinate, representing a peak in energy.
- Activated ComplexAnother term for the transition state, indicating the highest energy point in a reaction.
- Reaction CoordinateThe progress of a reaction pathway, typically represented along the x-axis of an energy diagram.
- Activation EnergyThe minimum energy required for a reaction to occur, measured from reactants to the transition state.
- Energy BarrierAnother term for activation energy, representing the energy threshold that must be overcome.
- Exothermic ProcessA reaction where energy is released, resulting in products that are lower in energy than reactants.
- Endothermic ProcessA reaction where energy is absorbed, resulting in products that are higher in energy than reactants.
- StabilityDetermined by the overall energy change, with lower energy indicating greater stability in reactions.
- ΔEThe overall energy change of a reaction, calculated as products minus reactants.
- ΔHThe change in thermal energy of a reaction, interchangeable with ΔE in energy diagrams.