- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

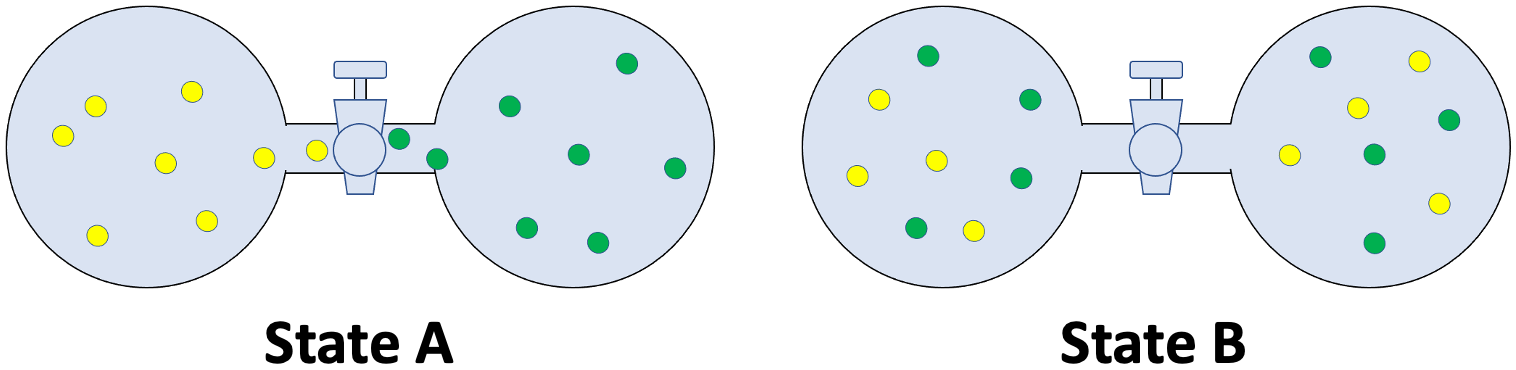
In state A, two ideal gases (represented by yellow and green spheres) initially occupy two separate bulbs. When the stopcock is opened, the two ideal gases went from state A to state B. Relate states A and B to the graph.

At constant temperature, an ideal gas undergoes expansion. Determine the signs (+, −, or 0) of ΔS, ΔH, and ΔG for this process.

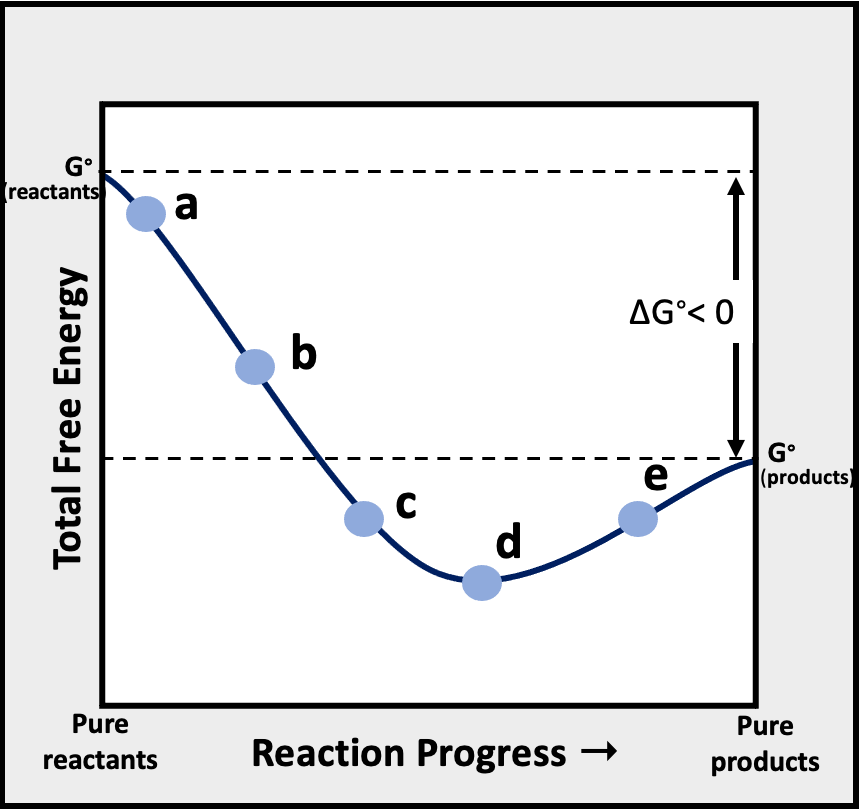
Determine at which point/s labeled a through e in the graph of the total free energy of reactants and products versus the reaction progress is Q > K.
Which of the following statement is true about the reaction shown below?
N2O4(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔH° = 58.02 kJ; ΔS° = 176.6 J/K
Predict which temperature condition is needed for the reaction below be spontaneous:
2 CO(g) + O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) (exothermic)
The following reaction is exothermic at constant pressure
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g)
Which of the following can be said about the reaction?
Shown below are system representations of three equilibrium mixtures for the interconversions of B molecules to X, B molecules to Y, and B molecules to Z. The molecules of B are shown as yellow spheres while molecules of X, Y, or Z are green spheres. Determine the sign of ΔG° for each case.
