(a) Which region of the periodic table shown here contains elements that are easiest to oxidize? (b) Which region contains the least readily oxidized elements?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Chapter 4, Problem 48e
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (e) Locate sulfur in the periodic table in Exercise 4.47; what region is it in?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the oxidation states of other atoms in the compounds mentioned in Exercise 4.47. Common oxidation states for elements like oxygen and hydrogen are -2 and +1, respectively.
Apply the rule that the sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound must equal zero. For polyatomic ions, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the charge of the ion.
For each compound, set up an equation where the sum of the oxidation numbers multiplied by their respective subscripts equals zero (or the charge of the ion). Include the known oxidation states and solve for the oxidation number of sulfur.
To locate sulfur in the periodic table, find it by its symbol 'S'. Note its group and period to determine the region it belongs to in the periodic table.
Identify the region (e.g., nonmetals, chalcogens) where sulfur is located and describe its general properties based on its position in the periodic table.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation Number
The oxidation number, or oxidation state, is a value assigned to an element in a compound that reflects its degree of oxidation or reduction. It indicates the number of electrons an atom gains, loses, or shares when forming chemical bonds. Understanding how to assign oxidation numbers is crucial for identifying redox reactions and balancing chemical equations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
Periodic Table Groups
The periodic table is organized into groups and periods, with elements in the same group sharing similar chemical properties. Sulfur is located in Group 16, also known as the chalcogens, which includes oxygen and selenium. This group is characterized by elements that typically have six valence electrons, influencing their reactivity and bonding behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course
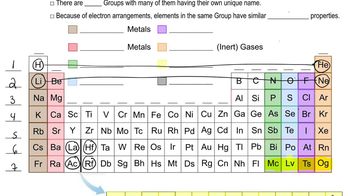
Periodic Table: Group Names
Chemical Bonding and Valence Electrons
Chemical bonding involves the interaction between atoms to form molecules, primarily through the sharing or transfer of valence electrons. The number of valence electrons determines how an element will bond with others. For sulfur, having six valence electrons allows it to form various compounds, influencing its oxidation states in different chemical environments.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Bonds
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1338
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (a) barium sulfate, BaSO4 (b) sulfurous acid, H2SO3 (c) strontium sulfide, SrS
470
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (d) hydrogen sulfide, H2S
524
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (f) Which region(s) of the periodic table contains elements that can adopt both positive and negative oxidation numbers?
710
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (a) S in SO3 (b) Ti in TiCl4
354
views
Textbook Question
Determine the oxidation number for the indicated element in each of the following substances: (c) P in AgPF6
758
views
