Silver chloride, often used in silver plating, contains 75.27% Ag by mass. Calculate the mass of silver chloride required to plate 155 mg of pure silver.
Write a ratio showing the relationship between the molar amounts of each element for each compound. (See Appendix IIA for color codes.) (a)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
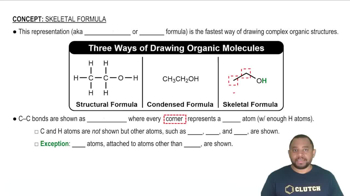
Key Concepts
Molar Ratio

Law of Definite Proportions

Chemical Formula
The iodide ion is a dietary mineral essential to good nutrition. In countries where potassium iodide is added to salt, iodine deficiency (or goiter) has been almost completely eliminated. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for iodine is 150 mg/day. How much potassium iodide (76.45% I) should you consume if you want to meet the RDA?
The American Dental Association recommends that an adult female should consume 3.0 mg of fluoride (F-) per day to prevent tooth decay. If the fluoride is consumed in the form of sodium fluoride (45.24% F), what amount of sodium fluoride contains the recommended amount of fluoride?
Write a ratio showing the relationship between the molar amounts of each element for each compound. (See Appendix IIA for color codes.) (b)
Determine the number of moles of hydrogen atoms in each sample. c. 2.4 mol C6H12
Determine the number of moles of hydrogen atoms in each sample. d. 1.87 mol C8H18
