Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rate Constant (k)
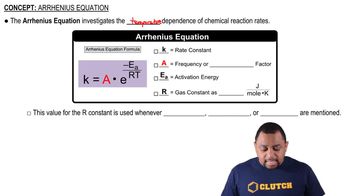
The rate constant (k) is a proportionality factor in the rate equation of a chemical reaction, indicating the speed of the reaction at a given temperature. It is influenced by factors such as temperature and the activation energy of the reaction. The units of k vary depending on the order of the reaction, and for first-order reactions, it is expressed in s⁻¹.
Recommended video:
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant of a reaction to the temperature and activation energy, expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT). Here, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation helps in understanding how temperature affects reaction rates and is essential for calculating the activation barrier.
Recommended video:
Activation Energy (Ea)
Activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to form products. A higher activation energy indicates a slower reaction rate, while a lower activation energy suggests a faster reaction. Understanding Ea is crucial for predicting how changes in temperature will affect the rate of a reaction.
Recommended video: