Textbook Question
Classify each property as intensive or extensive. a. volume b. boiling point c. temperature d. electrical conductivity e. energy
921
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

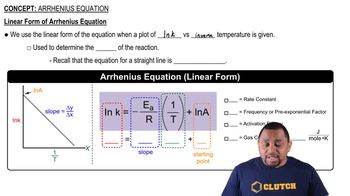

Classify each property as intensive or extensive. a. volume b. boiling point c. temperature d. electrical conductivity e. energy
At what temperatures are the readings on the Fahrenheit and Celsius thermometers the same?
Force is defined as mass times acceleration. Starting with SI base units, derive a unit for force. Using SI prefixes, suggest a convenient unit for the force resulting from a collision with a 10-ton trailer truck moving at 55 mi per hour and for the force resulting from the collision of a molecule of mass around 10 - 20 kg moving almost at the speed of light (3×108 m/s) with the wall of its container. (Assume a 1-second deceleration time for both collisions.)