One brand of laundry bleach is an aqueous solution containing 4.55% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) by mass. What is the molarity of this solution? (Assume a density of 1.02 g/mL.)
Ch.13 - Solutions
Chapter 13, Problem 69
Which beaker shows a greater decrease in liquid level after being left side by side on a lab bench for 1 week, a beaker with 100.0 mL of pure water or a beaker with 100.0 mL of seawater, and why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key difference between pure water and seawater: Pure water is composed solely of H2O molecules, while seawater contains dissolved salts and other substances.
Understand the concept of evaporation: Evaporation is the process where liquid molecules escape into the gas phase. It occurs more readily in pure substances due to fewer intermolecular forces compared to solutions.
Consider the effect of dissolved salts in seawater: The presence of salts in seawater increases the boiling point and decreases the vapor pressure compared to pure water, which means seawater evaporates more slowly.
Compare the evaporation rates: Since pure water has a higher vapor pressure than seawater, it will evaporate more quickly under the same conditions.
Conclude which beaker shows a greater decrease: The beaker with pure water will show a greater decrease in liquid level after one week due to its higher evaporation rate.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process by which molecules at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to enter the gas phase. It occurs at any temperature and is influenced by factors such as temperature, surface area, and humidity. In this context, both beakers will experience evaporation, but the rate may differ due to the composition of the liquids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
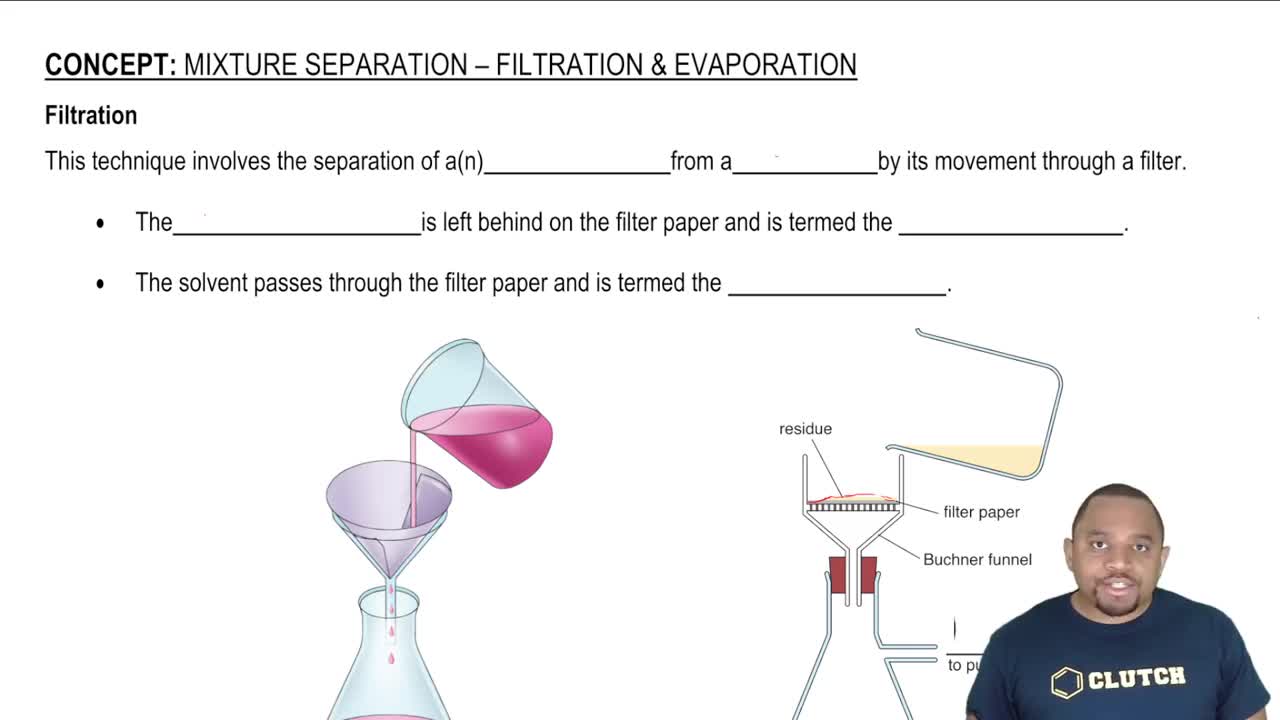
Filtration and Evaporation
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. Seawater contains dissolved salts, which lower the vapor pressure of the solution compared to pure water. This means that seawater will evaporate more slowly than pure water, leading to a smaller decrease in liquid level.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Colligative Properties
Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid or solid phase. Pure water has a higher vapor pressure than seawater due to the absence of solutes. As a result, the beaker with pure water will show a greater decrease in liquid level over time, as it evaporates more readily than the seawater, which has a lower vapor pressure due to the presence of dissolved salts.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1822
views
2
rank
Textbook Question
An aqueous solution contains 36% HCl by mass. Calculate the molality and mole fraction of the solution.
1601
views
Open Question
An aqueous solution contains 5.0% NaCl by mass. How do you calculate the molality and mole fraction of the solution?
Textbook Question
Which solution has the highest vapor pressure? a. 20.0 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in 100.0 mL of water b. 20.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11) in 100.0 mL of water c. 10.0 g of potassium acetate KC2H3O2 in 100.0 mL of water
2052
views
1
comments
Textbook Question
Calculate the vapor pressure of a solution containing 24.5 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) in 135 mL of water at 30.0 °C. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 31.8 torr. Assume that glycerin is not volatile and dissolves molecularly (i.e., it is not ionic), and use a density of 1.00 g/mL for the water.
3149
views
Open Question
A solution contains naphthalene (C10H8) dissolved in hexane (C6H14) at a concentration of 12.35% naphthalene by mass. Calculate the vapor pressure of hexane above the solution at 25 °C. The vapor pressure of pure hexane at 25 °C is 151 torr.
