Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is a stimulant found in coffee and tea. If a solution of caffeine in the solvent chloroform (CHCl3) has a concentration of 0.0500 m, calculate (b) the mole fraction of caffeine in the solution.
You make a solution of a nonvolatile solute with a liquid solvent. Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false.
a. The solid that forms as the solution freezes is nearly pure solute.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
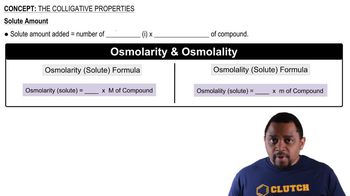
Colligative Properties
Freezing Point Depression

Purity of Crystals
Suppose that you want to use reverse osmosis to reduce the salt content of brackish water containing 0.22 M total salt concentration to a value of 0.01 M, thus rendering it usable for human consumption. What is the minimum pressure that needs to be applied in the permeators (Figure 13.26) to achieve this goal, assuming that the operation occurs at 298 K?
Assume that a portable reverse-osmosis apparatus operates on seawater, whose effective concentration (the concentration of dissolved ions) is 1.12 M, and that the desalinated water output has an effective molarity of about 0.02 M. What minimum pressure must be applied by hand pumping at 297 K to cause reverse osmosis to occur?
You make a solution of a nonvolatile solute with a liquid solvent. Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false.
b. The freezing point of the solution is independent of the concentration of the solute.
a. The vapor pressure of pure water at 60°C is 149 torr. What vapor pressure is predicted by Raoult’s law for a solution at 60°C that is 50 mol % water and 50 mol % ethylene glycol (a nonvolatile solute)?
At 63.5 °C, the vapor pressure of H2O is 175 torr, and that of ethanol (C2H5OH) is 400 torr. A solution is made by mixing equal masses of H2O and C2H5OH. (a) What is the mole fraction of ethanol in the solution?
