Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In the case of heptane, the two isomers can differ in the arrangement of carbon atoms, leading to variations in their physical properties, including viscosity. Understanding isomerism is crucial for predicting how structural differences affect the behavior of substances.
Recommended video:
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example
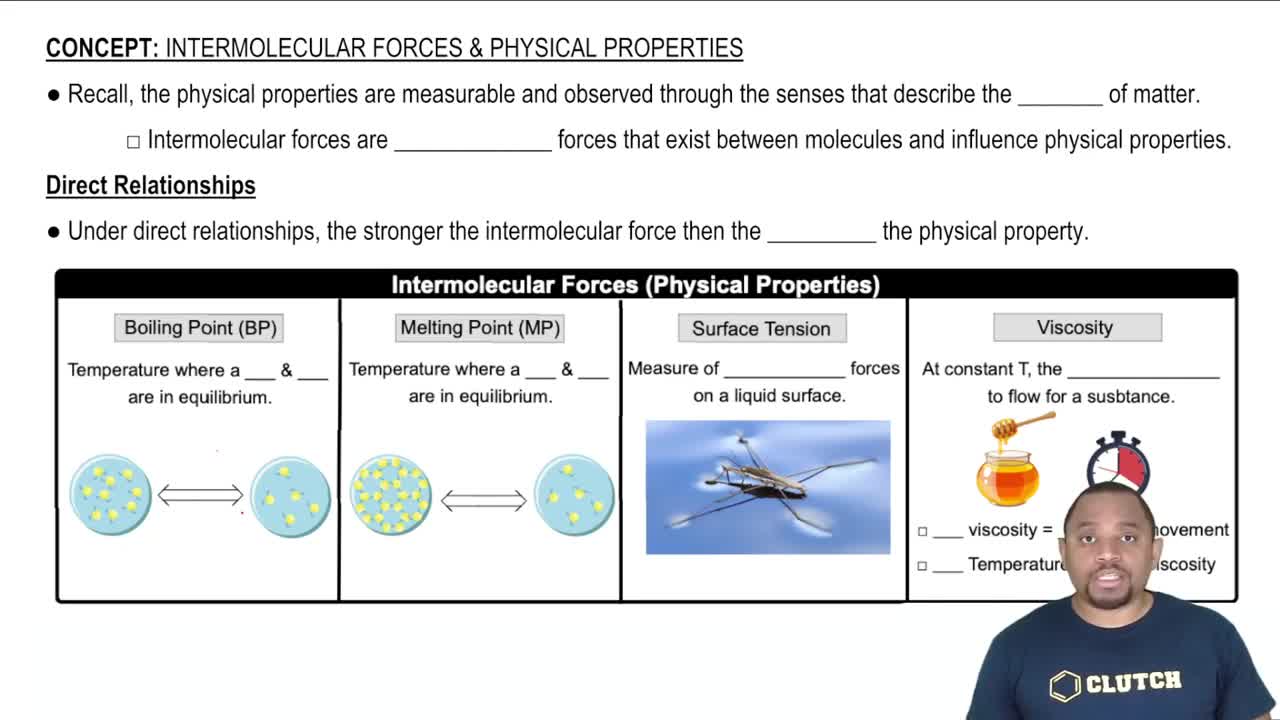
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is influenced by factors such as molecular size, shape, and intermolecular forces. Generally, larger and more complex molecules exhibit higher viscosity due to increased interactions between them. In the context of heptane isomers, the one with a more branched structure typically has lower viscosity compared to its straight-chain counterpart.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules that influence physical properties like boiling point, melting point, and viscosity. Stronger intermolecular forces lead to higher viscosity, as molecules are more tightly held together, making it harder for them to flow. In heptane isomers, the type and strength of these forces can vary based on molecular structure, affecting their overall viscosity.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces