Which of the following statements is false? (a) Gases are far less dense than liquids. (b) Gases are far more compressible than liquids. (c) Because liquid water and liquid carbon tetrachloride do not mix, neither do their vapors. (d) The volume occupied by a gas is determined by the volume of its container.
(c) Which is most likely to be a gas at room temperature and ordinary atmospheric pressure, F2, Br2, K2O?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceRecommended similar problem, with video answer:

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
States of Matter

Molecular Weight and Intermolecular Forces

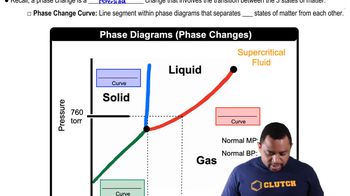
Phase Diagrams
(b) Which units are appropriate for expressing atmospheric pressures, N, Pa, atm, kg/m2?
A person weighing 75 kg is standing on a threelegged stool. The stool momentarily tilts so that the entire weight is on one foot. If the contact area of each foot is 5.0 cm2, calculate the pressure exerted on the underlying surface in (a) bars
A person weighing 75 kg is standing on a threelegged stool. The stool momentarily tilts so that the entire weight is on one foot. If the contact area of each foot is 5.0 cm2, calculate the pressure exerted on the underlying surface in (b) atmospheres
A person weighing 75 kg is standing on a threelegged stool. The stool momentarily tilts so that the entire weight is on one foot. If the contact area of each foot is 5.0 cm2, calculate the pressure exerted on the underlying surface in (c) pounds per square inch
